Vector DB Comparison
Overview of Vector DB Comparison
What is Vector DB Comparison?
Vector DB Comparison is a free and open-source tool developed by Superlinked to help users compare various vector databases. It offers a comprehensive table that outlines the features, licenses, development languages, and other attributes of different vector databases. This tool aims to simplify the process of selecting the most suitable vector database for specific AI and machine-learning projects.
What are the key features of Vector DB Comparison?
- Comprehensive Comparison Table: The core of the tool is an interactive table that allows users to compare vector databases side-by-side.
- Filter and Sort: Users can filter databases based on various criteria such as vendor, license, supported languages, and specific features like hybrid search or full-text search.
- Detailed Attributes: The table provides detailed information on each database, including its vendor, license type (e.g., Apache 2.0, MIT, Proprietary), supported development languages (e.g., Python, Java, C++), and launch year.
- Feature Verification: Each feature listed in the table has been verified to varying degrees by the community, providing a level of confidence in the accuracy of the information.
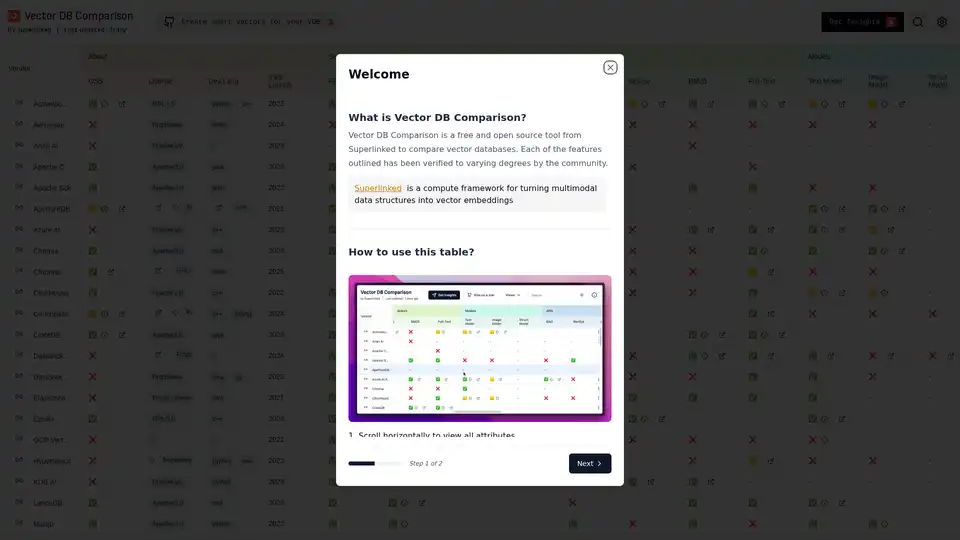
- Interactive Elements: The table includes interactive elements such as hoverable column headers for descriptions and sorting capabilities (single and multi-column sorting).
- Pinning Columns: Users can pin important columns next to the vendor column for easy comparison.
- Comments from Maintainers: Some cells include comments from maintainers, offering additional insights.
How does Vector DB Comparison work?
Vector DB Comparison works by aggregating and presenting data about different vector databases in a structured and easily navigable format. The key steps in its operation include:
- Data Collection: Superlinked gathers information about various vector databases, including their features, licensing, development languages, and other relevant attributes.
- Table Presentation: This information is then organized into a comprehensive table that allows users to compare databases side by side.
- Filtering and Sorting: Users can filter the table based on specific criteria to narrow down the list of databases that meet their requirements. They can also sort the table by column to prioritize certain attributes.
- Community Verification: The features listed in the table are verified by the community, ensuring a degree of accuracy and reliability.
- Interactive Elements: The table includes interactive elements such as hoverable column headers for descriptions and sorting capabilities.
How to use Vector DB Comparison?
- Access the Tool: Visit the Vector DB Comparison website.
- Explore the Table: Review the comprehensive comparison table, which lists various vector databases and their attributes.
- Filter and Sort: Use the filtering and sorting options to narrow down the list of databases based on your specific requirements.
- Pin Columns: Drag important columns next to the vendor column to keep them visible for easy comparison.
- Read Comments: Hover over cells with the info symbol to read comments from maintainers.
Why choose Vector DB Comparison?
- Comprehensive Information: Provides a wealth of information about various vector databases.
- Easy to Use: The interactive table and filtering options make it easy to compare databases.
- Community Verified: The features listed in the table are verified by the community, ensuring a degree of accuracy.
- Free and Open Source: The tool is free and open source, making it accessible to everyone.
Who is Vector DB Comparison for?
Vector DB Comparison is primarily intended for:
- AI and Machine Learning Engineers: Who need to select the most suitable vector database for their projects.
- Data Scientists: Who need to compare different vector databases based on their features and capabilities.
- Developers: Who need to choose a vector database for their applications.
- Researchers: Who need to evaluate different vector databases for their research projects.
Vector Database Selection: A Deep Dive
Choosing the right vector database is crucial for the performance and scalability of AI applications. Vector databases are designed to efficiently store, manage, and query high-dimensional vector embeddings generated by machine learning models. These embeddings capture the semantic meaning of data, allowing for similarity searches and other advanced analytics.
Here's a closer look at some of the vector databases listed in the Vector DB Comparison tool:
- Milvus: An open-source vector database designed for AI applications. It supports various distance metrics, indexing methods, and query types.
- Weaviate: An open-source, graph-based vector database that combines vector search with graph exploration. It's suitable for knowledge graphs and other applications that require both semantic and relational understanding.
- Pinecone: A managed vector database service that offers fast and scalable vector search. It's designed for production environments and supports various indexing methods and query types.
- Qdrant: An open-source vector similarity search engine that provides a simple and efficient way to store, search, and manage vector embeddings. It supports various distance metrics and indexing methods.
By using Vector DB Comparison, users can make informed decisions about which vector database is best suited for their specific use case. This can lead to improved performance, scalability, and overall success in their AI and machine learning projects.
Best Alternative Tools to "Vector DB Comparison"
YouTube-to-Chatbot is an open-source Python notebook that trains AI chatbots on entire YouTube channels using OpenAI, LangChain, and Pinecone. Ideal for creators to build engaging conversational agents from video content.
Reviewradar leverages AI to analyze over 5 million SaaS reviews, delivering instant user insights via a simple chatbot. Ideal for product managers seeking faster market research without interviews.
Find, compare, and choose from 4000+ APIs for AI, Web Scraping, SEO, Maps, Finance, and more. GetOData makes it easy to discover the best tools for your needs.
PubCompare is an AI-driven search engine for experimental protocols, enabling researchers to quickly find, compare, and validate protocols from scientific literature and vendor data, ensuring reproducibility and saving time.
Create AI-powered apps and AI agents that automatically plan and execute your tasks. Build your full-stack AI apps and monetize it with Momen's flexible GenAI app dev framework. Get started today!
Enhance APM with OpenLIT, an open-source platform on OpenTelemetry. Simplify AI development with unified traces and metrics in a powerful interface, optimizing LLM & GenAI observability.
Math AI is an AI-powered math solver that provides step-by-step solutions and explanations for various math problems. It supports photo input, advanced calculations, and personalized learning.

MintyCookie is an AI-powered matchmaking app connecting you with soulmates worldwide. Features include a universal translator, anonymous identity options, and AI-driven compatibility matching.
MyScale: AI database fusing vector search with SQL analytics. Unlock insights from vector datasets with speed and efficiency.
Milvus is an open-source vector database designed for GenAI applications, enabling high-speed similarity searches on massive datasets. It supports various deployment options, from lightweight local setups to scalable distributed solutions.

Weaviate is an AI-native vector database that simplifies building AI-powered applications. It offers features like semantic search, RAG and AI Agents. Trusted by AI innovators and scalable to billions vectors.
SvectorDB is a serverless vector database built for AWS, offering cost-effective vector search and seamless scaling from prototype to production.
Pinecone is a vector database that enables searching billions of items for similar matches in milliseconds, designed for building knowledgeable AI applications.
Infinity is an AI-native database designed for LLM applications, offering incredibly fast hybrid search across dense embeddings, sparse embeddings, tensors, and full-text. Achieve 0.1ms query latency on million-scale datasets.