Structurepedia
Overview of Structurepedia
What is Structurepedia?
Structurepedia represents a groundbreaking evolution in how we access and understand knowledge in the AI era. Imagine transforming the overwhelming flood of online information into clear, visual maps that mimic the way our brains organize ideas. This free platform redefines learning by offering structured, interactive knowledge trees for complex topics, powered by AI to make exploration intuitive and efficient. Unlike traditional encyclopedias or search engines that deliver linear text, Structurepedia visualizes the big picture first, allowing users to drill down into details with attached resources popping up seamlessly.
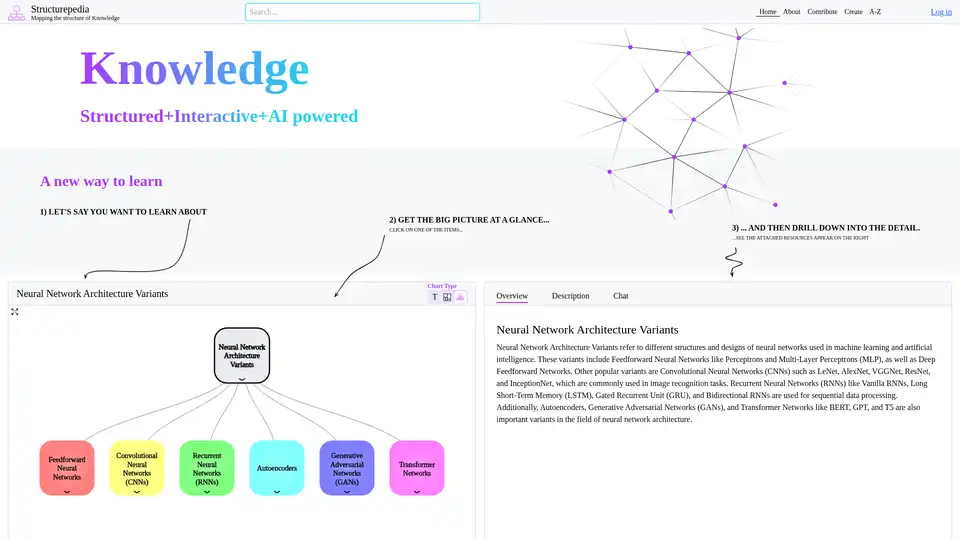
At its core, Structurepedia is an online encyclopedia of knowledge trees—dynamic diagrams that break down subjects into hierarchical structures. For instance, topics like "Neural Network Architecture Variants" are presented as interactive charts, covering everything from Feedforward Neural Networks (such as Perceptrons and Multi-Layer Perceptrons) to advanced models like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs: LeNet, AlexNet, VGGNet, ResNet, InceptionNet), Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs: Vanilla RNNs, LSTMs, GRUs), Autoencoders, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), and Transformer Networks (BERT, GPT, T5). These visualizations aren't static; they're AI-enhanced for interactivity, enabling users to click through layers and access linked resources on the right side of the interface.
How Does Structurepedia Work?
The platform operates on a simple yet powerful principle: knowledge isn't linear, so why present it that way? Structurepedia starts with a high-level overview—a snapshot of the topic's structure. Users can then interact by clicking on nodes to expand into subtopics, revealing deeper insights and relevant attachments like articles, videos, or datasets. AI plays a pivotal role here, suggesting improved query formulations via StructureBot, which refines searches for better accuracy. This AI assistance ensures that even vague inputs lead to precise, structured outputs.
Navigation is user-friendly: The homepage features sections like Home, About, Contribute, Create, and A-Z for browsing. Logging in allows personalized interactions, while the full-screen mode immerses users in explorations. For example, when delving into neural networks, the chart type (T for tree-like) displays variants with editable snapshots, overviews, descriptions, and even a chat feature for quick queries. The philosophy behind this is rooted in cognitive science—mimicking mental models to accelerate comprehension and retention.
Contributors build the ecosystem voluntarily, expanding the table of contents with diagrams on diverse subjects like types of clouds, the Suez Canal, or popular music production DAWs. AI aids in generation, but manual labor follows guides for precision. The content is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike, fostering a collaborative, open community.
How to Use Structurepedia?
Getting started is straightforward and requires no downloads—it's a web-based tool accessible from any browser.
- Search Visually: Enter a topic, like "neural network architectures," and get an instant big-picture diagram.
- Interact and Explore: Click on elements (e.g., CNNs) to drill down. Resources appear dynamically on the right, including overviews, technical descriptions, and chat options for AI-assisted explanations.
- Contribute or Create: Use the Contribute section to add diagrams following the guide, or leverage StructureBot for AI-suggested enhancements. Manual editing ensures quality.
- Browse the A-Z Index: Discover pre-built trees on AI, machine learning, and beyond.
For optimal use, enable full-screen for immersive sessions, and join the community via X/Twitter or Discord for updates and collaborations.
Why Choose Structurepedia?
In a world saturated with information, Structurepedia stands out by prioritizing structure over volume. Traditional resources like books or Wikipedia often bury hierarchies in paragraphs, slowing learning. Here, AI-powered visuals cut through the noise, making complex fields like machine learning accessible at a glance. It's free, resource-rich, and interactive—ideal for visual learners who benefit from mind-map-style representations.
Key advantages include:
- Efficiency: Get the overview instantly, then zoom into details without endless scrolling.
- AI Integration: StructureBot refines queries, while the platform suggests expansions, blending human curation with machine intelligence.
- Community-Driven Growth: With voluntary contributions, the library expands steadily, covering AI topics deeply (e.g., Transformer models like GPT for natural language processing).
- Educational Value: Enhances retention by aligning with how knowledge is stored in the brain—through interconnected nodes rather than isolated facts.
Compared to tools like mind-mapping apps, Structurepedia is specialized for encyclopedic depth, especially in AI and technical domains. It's not just a tool; it's a learning paradigm shift.
Who is Structurepedia For?
This platform caters to a wide audience seeking deeper understanding without the overwhelm:
- Students and Researchers: Ideal for tackling intricate subjects like neural network variants in machine learning courses or AI research. Visualize architectures to grasp differences between RNNs for sequential data and CNNs for images.
- Professionals in AI/ML: Engineers and data scientists can use it for quick refreshers on models like GANs for generative tasks or Transformers for NLP, with resources linking to implementations.
- Lifelong Learners: Anyone curious about complex topics— from cloud types to historical events—benefits from the visual, interactive format.
- Educators and Trainers: Create custom trees for lessons, leveraging AI suggestions to build engaging materials.
It's particularly valuable for those in AI-related fields, where understanding architectures (e.g., how LSTMs handle long-term dependencies) can inform projects or career decisions.
Best Ways to Maximize Structurepedia for AI Learning
To get the most out of it:
- Combine with Practice: After exploring a neural network tree, apply concepts in coding environments— the resources often point to tutorials.
- Collaborate: Contribute to trees on emerging AI topics, like new Transformer variants, to stay ahead.
- Integrate with Searches: Use it alongside traditional engines; start with Structurepedia for structure, then dive into specifics.
User experiences highlight its transformative impact: Learners report faster topic mastery, with diagrams clarifying relationships that text alone obscures. For AI enthusiasts, sections on GANs or BERT provide practical insights into real-world applications, from image synthesis to language models.
In summary, Structurepedia isn't just another resource—it's an AI-empowered gateway to structured knowledge, empowering users to navigate complexity with clarity. Whether you're decoding neural architectures or branching into new domains, this tool accelerates discovery and deepens expertise.
Best Alternative Tools to "Structurepedia"
Dialzara provides an AI receptionist that handles unlimited calls, books appointments, and captures leads 24/7. Set up in minutes and enjoy a 7-day free trial.
Squad AI is an AI-powered product management platform designed to streamline product discovery, strategy, and roadmapping. It helps teams align on goals, understand customer feedback, and build user-centric products effectively.
Forethought's multi-agent system transforms customer support with AI, resolving inquiries, triaging tickets, and guiding agents, boosting efficiency and customer satisfaction.
FlowCraft is an AI-powered diagramming tool that transforms text descriptions into stunning visuals including flowcharts, infographics, and concept diagrams. Perfect for content creators, business professionals, and educators.
From internal SOPs to interactive product walkthroughs, Guidejar helps teams create how-to guides that scale knowledge and reduce repeat questions.

Use ChatGPT for free without registration. Experience advanced AI technology without any restrictions. Access the latest GPT models and get assistance with various tasks.
Rationale is a GPT-powered AI tool that analyzes decisions with pros/cons, SWOT, cost-benefit, and multi-option techniques. Get quick, personalized insights to make rational choices in business or personal life.
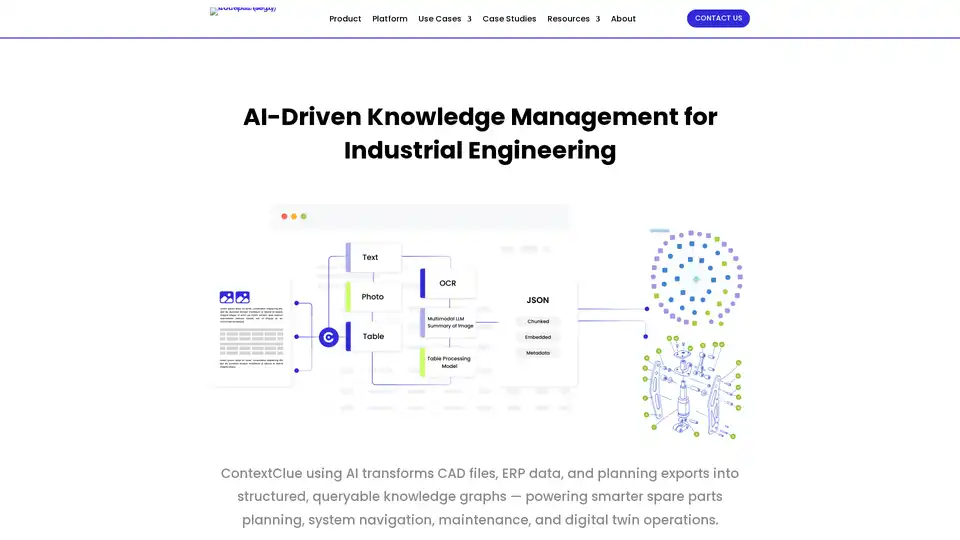
Optimize engineering workflows with intelligent knowledge management – organize, search, and share technical data across your entire ecosystem using ContextClue's AI-powered tools for knowledge graphs and digital twins.
Jungle is an AI-powered study tool that instantly generates flashcards, multiple-choice questions, and more from lecture slides, PDFs, and videos. Join over 1 million students revolutionizing their learning with spaced repetition and personalized quizzes.
Discover Knowmax, the AI-guided knowledge management platform for CX teams. It unifies knowledge, creates interactive decision trees, and empowers self-service, reducing answer time by 80% and boosting CSAT by 30%. Ideal for telecom, banking, and more.
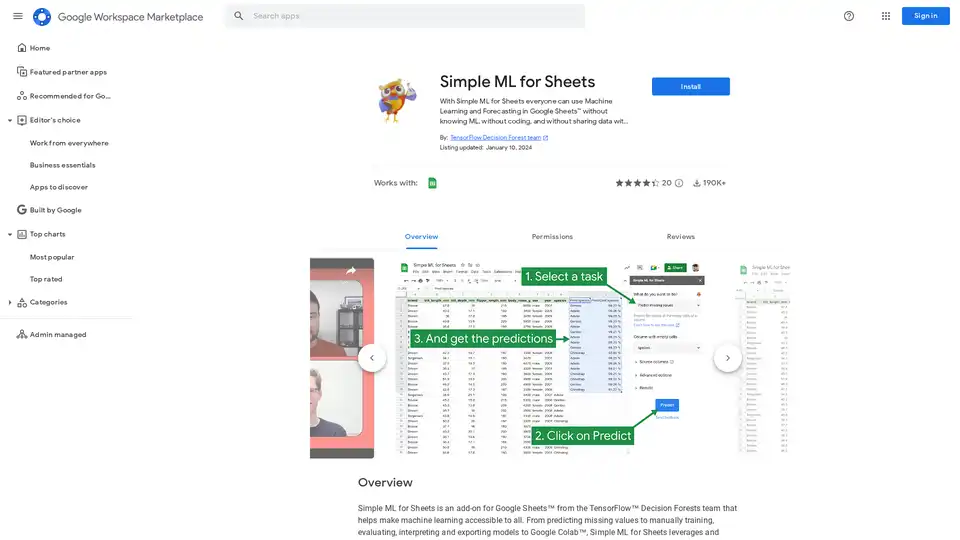
With Simple ML for Sheets everyone can use Machine Learning and Forecasting in Google Sheets™ without knowing ML, without coding, and without sharing data with third parties.
Bring your virtual avatars to life. Create & interact with your own customizable avatar. Features advanced AI powered, context driven facial expressions, gestures and poses that respond to your every word and action.
Rose AI is a unified data platform for finance that simplifies data discovery, visualization, and analysis with AI agents and natural language querying.
TextGPT: Access ChatGPT & Dall-E via text. Get quick answers & generate images. Simple, powerful AI tool.